2 key points in the R&D of semaglutide and its oral formulations

In September 2019, the world's first non injectable GLP-1RA oral Semaglutide tablet was approved by the FDA for marketing. It was taken once a day in the stomach half an hour before breakfast to improve the blood sugar control of adult patients with type II diabetes by combining diet control and exercise.
The appearance of Semaglutide oral preparation has changed the administration mode of GLP-1RA drug, which reduces the trauma of administration for diabetic patients, and improves drug compliance and convenience.
In the development process of semaglutide and its oral formulations, there are two key points: one is how to improve the drug half-life, and the other is how to achieve oral administration. Firstly, in order to address the drawback of short half-life of peptides, amino acids at the enzyme binding site are replaced to resist enzymatic hydrolysis; Linking fatty acid side chains to enhance binding with albumin, thereby delaying systemic clearance and achieving long-lasting effects.
In order to achieve oral administration, a small molecule absorption enhancer was used to successfully achieve sufficient bioavailability of oral semaglutide. SNAC (a new small molecule absorption enhancer) can locally increase the pH value in the stomach, prevent the degradation of semaglutide by peptidases in the stomach, and promote the absorption of semaglutide, breaking through the limitation that peptides cannot be absorbed orally.
Fast Link
>> Custom Peptide Synthesis Inquiry
>> Semaglutide API & Impurities
Development of Subcutaneous Injection Formulation of Semaglutide
Semaglutide, developed by Novo Nordisk, was initially designed as a powerful and lasting subcutaneous injection anti diabetes drug, with the frequency of once a week to improve convenience.
Semaglutide was approved for market by the FDA in December 2017, making it the seventh GLP-1RA approved globally after Exenatide, Liraglutide, Albiglutide, Dulaglutide, Lixisenatide, and Benaglutide (visit www.omizzur.com to learn more about peptide synthesis) .
As Novo Nordisk's second GLP-1 RA drug, the development strategy of Semaglutide draws on the company's first GLP-1 RA drug, Liraglutide, by modifying the sequence structure of endogenous GLP-1 and extending the plasma half-life by binding fatty acid side chains to human albumin on the peptide backbone.
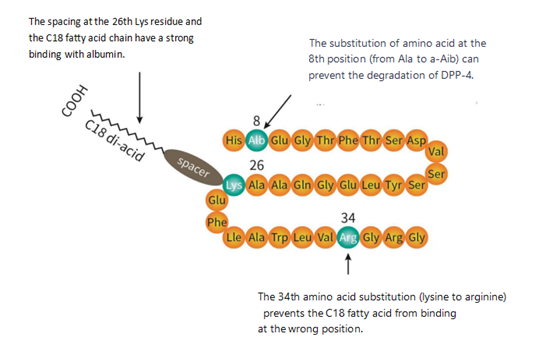
Specifically, first of all, semaglutide takes the sequence and structure of endogenous GLP-1 as the starting point to reduce the risk of immunogenicity. Subsequently, through alanine scanning mutation technology, researchers found that replacing the endogenous 8th alanine of GLP-1 with alpha aminoisobutyric acid (a non natural amino acid) not only maintained the affinity of the drug for GLP-1 receptor binding, but also protected the peptide from degradation by DPP-4 at the N-terminus.
However, in experiments involving fatty acid modification, researchers found that the strong affinity between GLP-1RA and albumin affects the binding of GLP-1RA to GLP receptors. Therefore, balancing the relationship between half-life and efficacy is a crucial issue. After extensive screening and comparison of linkers and fatty acids, it was finally determined that modifying lysine 26 with a gamma Glu-2xOEG linker and a C18 binary fatty acid side chain can simultaneously ensure high affinity for albumin and high efficacy for GLP-1 receptors.
In addition, researchers also replaced lysine at position 34 with arginine to prevent the fatty acid side chain from connecting to the wrong position. The molecular schematic diagram of Semaglutide is shown in the figure. Its affinity for GLP-1 receptors is 0.38 ± 0.06 nM, which is 3 times weaker than that of Liraglutide. However, its affinity for albumin is six times that of Liraglutide, and its half-life in the human body is as long as 165 hours.
Development of Semaglutide Oral Preparation
From subcutaneous injection to oral administration of semaglutide, it is far more difficult than imagined. The abundant proteases in the gastrointestinal tract can rapidly hydrolyze peptides, and peptide drugs have high molecular weight, low permeability, and difficult absorption, making oral administration extremely difficult
Previously, the majority of GLP-1RA drugs that had been marketed were administered subcutaneously. However, from the perspective of convenient medication for patients, oral administration is a fairly ideal delivery method. Oral medications are usually small molecules that require a certain degree of hydrophobicity. For GLP-1 RA, one approach is to develop small molecule agonists that activate GLP-1 receptors, but the efficacy of small molecule agonists is insufficient, they lack specificity for binding to GLP-1 R, and their half-life is not ideal.
Another strategy is to use absorption enhancers. N - [8- (2-hydroxybenzoyl) amino] octanoate (SNAC) developed by Emisphere is a recognized safe small molecule absorption enhancer that can assist in oral drug delivery. SNAC is not active in the pharmaceutical field and is mainly used as a food supplement, vitamin, and dietary ingredient. SNAC has previously been used in combination with heparin, ibandronate, and vitamin B12 to increase drug absorption.
The oral formulation of semaglutide is a formula composed of SNAC. Peptide drugs are mainly absorbed in the intestine, and oral administration of semaglutide changes the absorption site of the peptide, allowing it to be absorbed in the stomach rather than in the intestine. During absorption, the dissolution of SNAC in the stomach can locally increase the pH value of the stomach, thereby increasing the solubility of semaglutide and changing the acidic environment in the stomach to a neutral environment, inactivating peptidases and avoiding degradation of semaglutide by peptidases in the stomach.
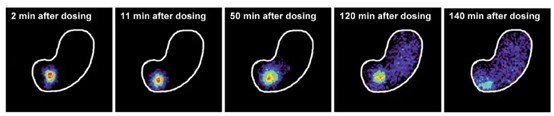
Experiments have shown that the lipophilicity of SNAC allows it to be embedded into the cell membrane, aiding in the rapid absorption of semaglutide by cells After oral administration of semaglutide, splenic vein blood and hepatic portal vein blood were collected separately.
The results showed that the concentration of semaglutide in the splenic vein was much higher than that in the hepatic portal vein, indicating that the initial uptake of semaglutide occurred in the stomach rather than the small intestine. The dissolution of semaglutide in the stomach is shown in the figure:
 Order Peptide Now:
Order Peptide Now:1. Click to send inqauiry online: Make Inquiry Now
2. Send mail to us: [email protected]
* Please mail us product name and quantity needed, Omizzur will get back to you within 1 hour.
Read Related Articles:
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap